
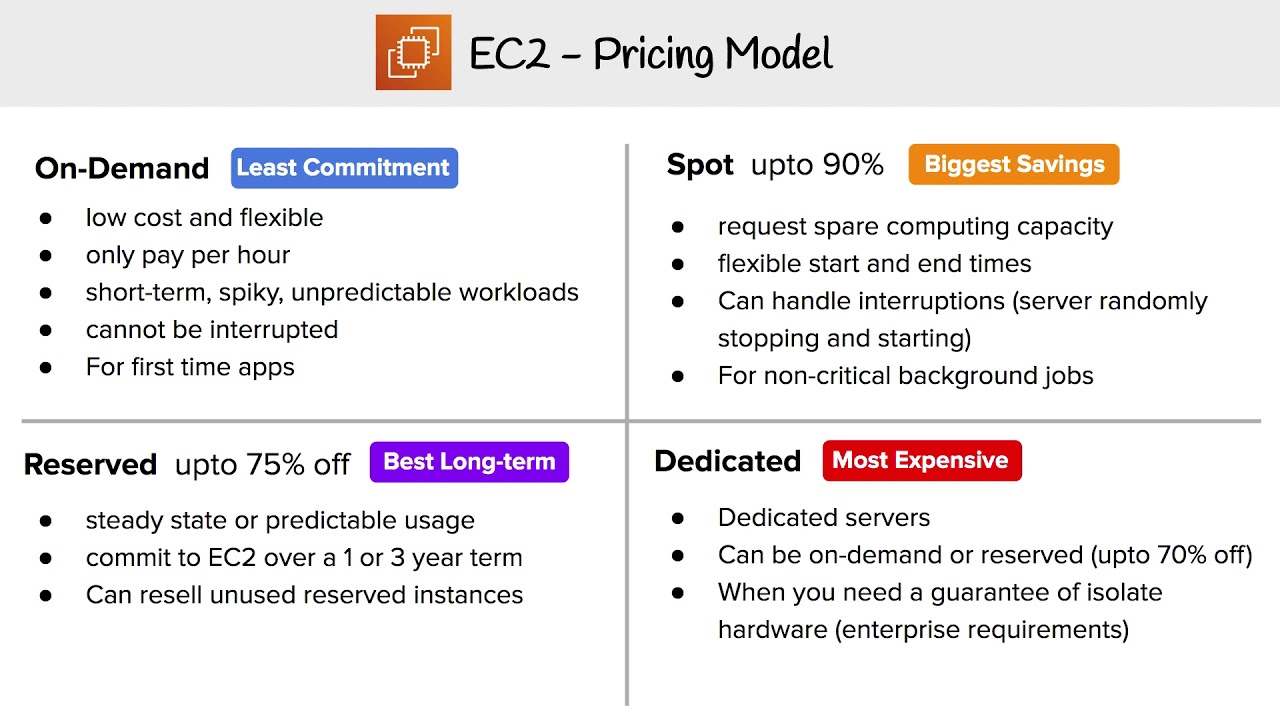
For example, there are several AWS backup options including the AWS Backup service and storage services like S3, Glacier, EBS, EFS, etc. Amazon also provides a plethora of services and options for most use cases, allowing you to switch to a service that meets your need at a lower cost. Amazon S3 and many other services offer tiered pricing, and Amazon EC2 offers volume discounts for users who spend more than $500,000 in upfront costs. The Principle: AWS provides volume discounts. Truth be told, most servers don’t have huge peaks or troughs in their usage - and running them on dedicated hosting or on-prem will be a lot cheaper than on Amazon. If you want to really “pay as you go”, you’ll have to settle for Amazon’s On-Demand Pricing, which becomes quite expensive even for small workloads, when used for ongoing server deployments. Pay per use is great because it eliminates overcapacity and wasted computing resources. The Good: It’s why organizations started moving to the cloud. It also provides extreme flexibility - you can order 1,000 machines for an hour and then stop them and pay only for those 1,000 machine hours. AWS is dedicated to turning your CapEx expenses into OpEx.
The Principle: This is the main idea behind AWS - instead of buying or building costly infrastructure, rent it. In this article we'll review the five principles and provide a grain of salt you should consider before hooking into the Amazon machine.

These principles provide immense benefits and efficiencies for thousands of organizations, which has driven AWS’s stellar growth.
AWS PRICING MODELS FREE
Amazon Web Services advertises four principles that guide their pricing strategy - pay as you go, pay less by using more, save when you reserve, and their free tier.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
